Navigating the e-QMS Landscape: Insights from the European SaMD Meetup
Ivo Flipse from MedQAIR co-hosted the European SaMD Meetup alongside Lara Rashdan from hema.to. In this session, industry experts, vendors, and users gathered to discuss the evolving landscape of electronic Quality Management Systems (e-QMS). The conversation centered around vendor capabilities, user experiences, and alternative quality management setups. This discussion provided valuable insights into how organizations can navigate compliance while improving efficiency in their quality management processes.
Vendor Perspectives: Innovations in e-QMS
Four leading e-QMS providers—Formly, Matrix Requirements, OpenRegulatory, and Qualio—shared how their platforms help companies manage quality and regulatory compliance efficiently.
Formly: AI-Driven Compliance
Formly showcased its AI-powered e-QMS designed to simplify regulatory documentation. The platform’s roadmap supports users in managing compliance tasks such as training and supplier management while guiding them through technical documentation development. CEO Spencer emphasized that AI provides
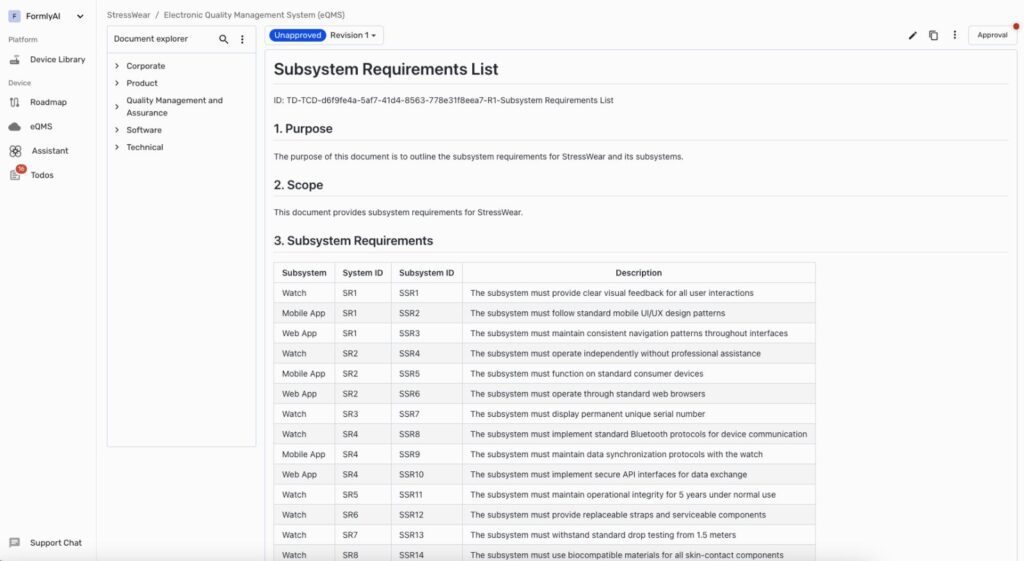
Formly takes an approach similar to Vanta. They offer a roadmap to demonstrate compliance with a certain standard and have broken it down into many small tasks. Each task functions as a mini-questionnaire with guidance and, where possible, built-in AI assistants to help users provide the correct answers.
Overall, Formly’s approach differs significantly from the more traditional document-based user experience of other e-QMS solutions.
Matrix Requirements: Bridging Engineering and Quality
Matrix Requirements introduced its item-based approach to design control and QMS documentation, offering a more flexible alternative to traditional document-driven systems. Instead of static documents, requirements, risks, test cases, and other quality records are stored in a structured database. This allows users to construct documents dynamically by querying the database and customizing the layout using lists or tables.
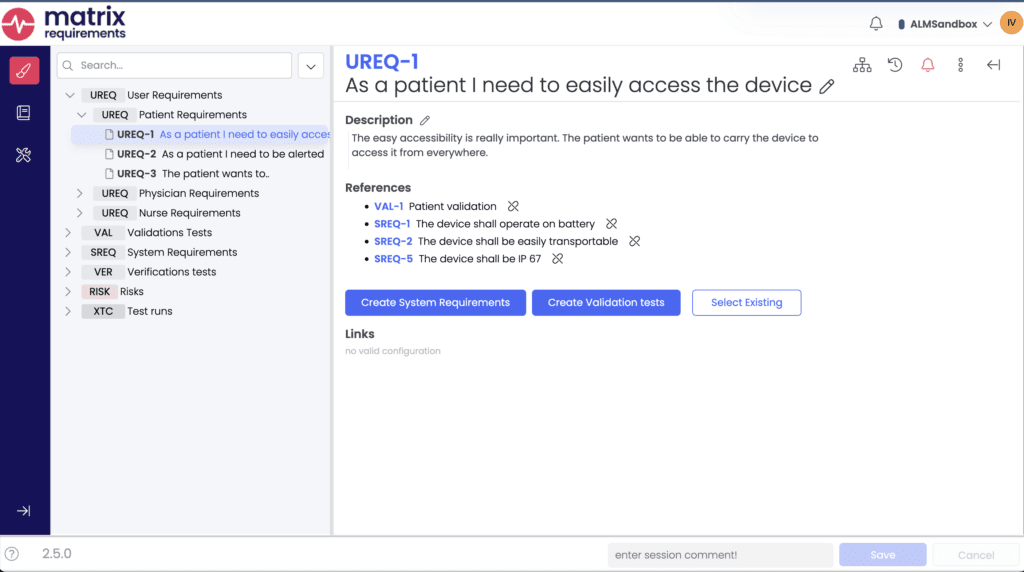
Matrix is highly flexible, allowing users to configure their own document structures and item attributes such as text fields and dropdowns. However, significant customization is required if deviating from their preconfigured templates. Additionally, Matrix Requirements has recently started experimenting with AI to automate aspects of risk management, aiding in the generation of risk assessments.
Users appreciated Matrix’s two-way Jira integration, which facilitates seamless linking between quality records and development workflows, allowing engineering and regulatory teams to collaborate effectively while maintaining full traceability.
OpenRegulatory: Practical and Cost-Effective Solutions
OpenRegulatory presented Formwork, a lightweight e-QMS solution designed for startups. Formwork provides structured templates that support compliance with MDR and FDA regulations while remaining cost-effective. Unlike Matrix Requirements, Formwork includes built-in support for SOP templates, CAPAs, and training management without requiring additional modules.
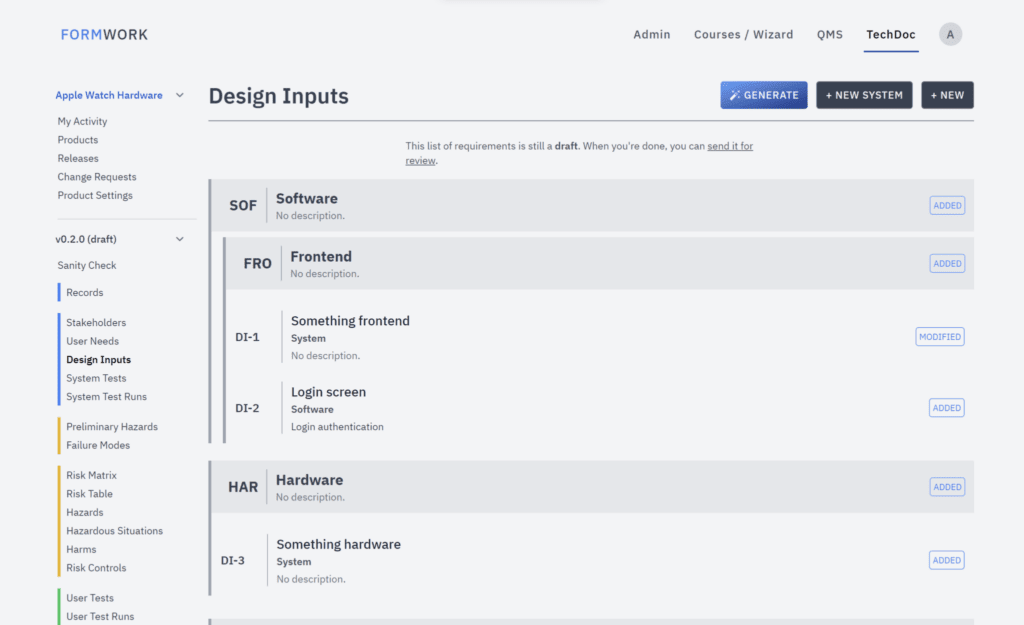
While the platform does offer automated reminders, this is a feature common across other e-QMS solutions. A notable difference is that Formwork offers less flexibility compared to other platforms. The system follows a rigid structure—our way or the highway. This means that if companies need additional compliance frameworks, such as ISO 27001, they may find Formwork limiting. However, this limitation is not unique to Formwork, as Formly also follows a similar approach.
Qualio: A Comprehensive Quality Management Platform
Qualio highlighted its all-in-one e-QMS, emphasizing automation, collaboration, and AI-assisted documentation. The platform offers a comprehensive set of features, including document control, training, purchasing, and design control, all available out of the box. Like all other systems, Qualio provides 21 CFR Part 11 compliant electronic signatures.
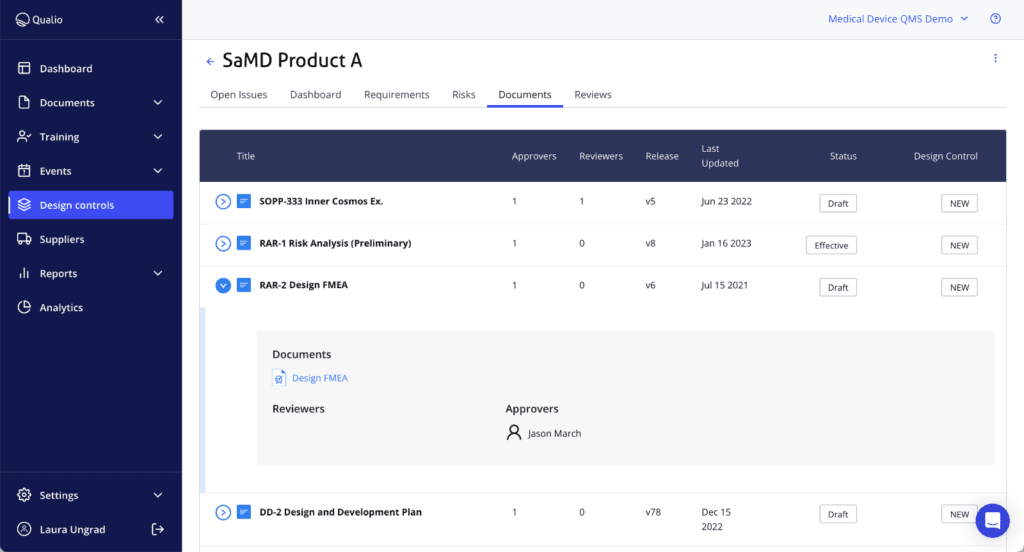
Additionally, Qualio comes preloaded with templates for QMS and risk management, making it easier for organizations to establish compliance frameworks. Notably, it also supports ISO 27001 compliance natively, unlike most competitors. While Matrix Requirements can be configured to achieve the same, it requires additional customization.
Alternative Setups: DIY Quality Management
While vendor solutions offer structured compliance support, some companies have successfully implemented alternative QMS setups using widely available tools such as GitHub, Jira, and Confluence.
GitHub-Powered QMS
Liliana from Tensor Medical shared how her team built a fully functional QMS using GitHub, modeled after Ivo’s experience at Zimmer Biomet. All their QMS and Technical Documentation reside alongside their SaMD source code on GitHub, leveraging automation for document versioning, electronic signatures, and training management.
Tensor Medical utilizes GitHub Actions and issue tags to trigger various automations, ensuring smooth workflow management. One of the key benefits of their approach is the ability to properly branch requirements and technical documentation using GitHub’s version control system. This ensures that requirement changes stay synchronized with code changes—if a code change isn’t merged, the associated documentation updates are also left unmerged.
Additionally, version control becomes particularly powerful, as every change made to a document can be tracked with full transparency regarding who made what changes and when. While other systems, such as Matrix Requirements, also offer extensive audit trails, GitHub’s approach provides a native and highly effective version control system. However, the downside is that everyone working on the documentation needs to be comfortable editing text files and working with Git. That said, software developers will generally love the setup.
Liliana demonstrated the process of creating a new document by opening a GitHub Issue, which then triggered multiple integrations. Another significant advantage of their setup is that every pull request can generate a live web-based version of all changes to the QMS or Technical Documentation, allowing multiple versions to be reviewed in parallel with ease.
Jira and Confluence Workflow
Pascal explained that Jira and Confluence are not e-QMS platforms per se, but with the right plugins, they can be adapted for quality management. Confluence is particularly useful for managing documents and more complex records, while Jira—traditionally a ticket management tool—can be heavily customized, much like Matrix Requirements. However, extensive configuration can be time-consuming.
Jira excels at managing records and integrates well with GitHub, making it a popular choice for organizations where software developers are already familiar with the tool. Some recommended plugins for enhancing Jira and Confluence for QMS purposes include:
- Document Control: Comala
- Nicely Formatted Exports: Scroll PDF Exporter
- Traceability Matrices: Jira Snapshots
- Test Management: Xray
- Drawings: draw.io
Due to its flexibility, Jira and Confluence can be used for various compliance standards, including ISO 27001, and can be tailored to specific needs. The platforms also offer a flexible automation engine and API access, enabling complex analyses and integrations.
Final Thoughts
At the end of the meetup, there was time for discussion and sharing user experiences. One key concern raised was pricing, which has led some teams, such as Tensor Medical, to develop their own QMS solutions.
Another question focused on whether e-QMS platforms effectively support both software and hardware development, as some solutions are tailored specifically to SaMD and lack the flexibility to exclude software requirements when necessary.
Most Requested Features
- Matrix Requirements: More collaboration at the review level, making it easier to comment and manage document reviews. (As a user of Matrix, Ivo seconds this feature request.)
- Formly: More integrations with other tools, as they have kept it agnostic so far. Additionally, better collaboration tools and change management capabilities to guide users effectively.
- Formwork: With 50 points on their backlog, the two highest priorities are project management (similar to Jira) and a PMS module to track trending data, generate PMS reports, and manage feedback.
- Qualio: While Qualio already integrates with many platforms, clients continuously request more integrations.
Industry Trends
- AI in QMS: Bringing more AI-driven assistants to simplify processes, but ensuring it is implemented correctly remains a challenge.
- Usability Improvements: Making tools more intuitive so that smaller teams can maximize efficiency. According to Spencer, this likely requires tools to be more opinionated to streamline workflows effectively.
Implementation Timeframe
How long does it take to set up and configure an e-QMS solution? It varies by system. Highly flexible tools take longer to configure, while more opinionated solutions enable quicker deployment. However, if a tool’s default setup doesn’t align with a company’s needs, it might not be the right fit.
Balancing Guidance and Understanding
A final question from Ivo addressed the risk of overly guided tools. Some platforms offer extensive hand holding, but users may not fully understand what they are doing. This sparked an engaging discussion. For example, Formly provides structured tasks and chat-based support to assist users in real time.
The meetup highlighted the diverse approaches organizations take to quality management—from structured vendor-driven solutions to fully customized setups. While traditional e-QMS platforms provide automation and regulatory support, alternative approaches offer cost-effective flexibility. As the industry evolves, organizations must balance automation, integration, and usability to ensure successful quality management.
For those looking to implement or improve their e-QMS, understanding their team’s specific needs and regulatory requirements will be key in selecting the right solution.




